Digitalization and growth of hybrid/mobile working models lead to massive increase in users accessing business information though insufficiently secured web browsers using public networks. We search for information – using the Web. We store private information – on the Web. With that, a major attack vector for cyberthreats today is the Web browser.
For years companies spent a lot of effort to protect their networks from unauthorized access. With people increasingly working from home using VPN connections to company resources while using their browser to access all sort of information it has just become easier for criminals as the number of devices and identities on the public network has grown exponentially. Phishing as well as malicious code embedded in websites or documents you download is a fairly easy method to ‘succeed’ on a certain percentage if you target thousands or even millions of devices. Someone will always accept that ‘friendly invitation’ or use a device that is not sufficiently protected. But what is “sufficient” ? Classic security methods rely on ‘knowing the fingerprint of a threat’. As there is a constant stream of new malware, companies have switched to full blocking with some whitelisted ‘known good sites’ but this will often block users from accessing relevant information for productive work.
‘Zero Trust the Web’ – by Browser Isolation
A fast growing technology that aims to resolve this is ‘Browser Isolation’ (also known as ‘Web Isolation’). Browser Isolation operates within a self-contained “airtight” browsing session that prevents malware and other malicious content from accessing anything outside of those confines . Unlike antivirus solutions, which attempt to identify and quarantine malware after it’s already been saved to the computer, browser isolation follows a Zero Trust approach that assumes all web content is untrusted and therefore high risk.
Because of its practicality and effectiveness, browser isolation is now regarded by Experts and Analysts as a best practice when it comes to hardening web security and establishing a secure web gateway.
Technologies
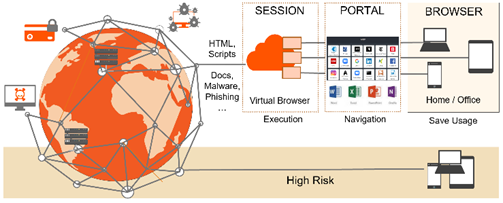
All Browser Isolation (BI) strategies intend to move the user’s browsing activity to an isolated environment that is somehow separated from the endpoint device. That leaves malware delivered through web to that sandbox with no connection to user, data or endpoint itself.
Current BI solutions come in two different technology approaches:
- Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) makes use of cloud security principles. When an end user accesses a web page, the web content is actually loaded on a remote server and the users device is only presented a rendered version of the page without active content. Depending on vendor, the solutions support Cloud based as well as in-house servers.
- Client-side BI separates web content using client side virtualization or sandboxing code.
All BI solutions delete at the end of a session associated data in the sandbox and with that also any associated malicious content.
Technology strength and weaknesses
While a strong advantage of Client-side BI is the use of the endpoints local processing power for its function, this also means that there is a piece of additional software to be installed and maintained on the users device – making it platform dependent and ‘high maintenance’.
The strong plus on Remote Browser Isolation is that it needs no changes on the endpoint and works with modern browsers on any device. This comes however at the price of processing power in a scalable Cloud infrastructure.
Base of your Digital Workspace
On a broader view – Browser Isolation should be seen as the base of your future, endpoint- and location-agnostic Digital Workspace, where most services are accessed through Remote Browser Isolation – enhanced with virtualized legacy Windows Apps delivered through the browser too.
Talk to us if you want to look at future today.
